Tech
A Comprehensive Guide to Snapdragon’s 5nm Processors
In the rapid progression of digital age, semiconductor technology has been a key driver of advancement. Chipmakers strive to make smaller, faster, and more efficient processors. Qualcomm’s Snapdragon has been leading the race, particularly with its 5nm processors. In this guide, we will dive deep into these processors, unravel their distinct features, and understand their implications for the future.
The term “5nm processor” signifies a chip manufactured using a 5-nanometer (nm) process technology. The “5nm” stands for the size of transistors and other microscopic components within the chip, which, in turn, influences the processor’s performance and energy consumption.
Understanding the Technology: 5nm Processors
A “nanometer” is a unit of length equal to one billionth of a meter. When used in the context of semiconductor manufacturing, it describes the size of the transistors and other components that make up a processor. Smaller transistor sizes allow for more transistors to be packed onto a single chip, thus enhancing its performance, energy efficiency, and functionality.
The transition to 5nm technology represents a significant leap forward. This smaller scale has allowed for increased transistor density, leading to processors that can perform more operations per second, all while consuming less power. Not only does this technology improve performance and energy efficiency, but it also opens the door to more sophisticated features such as advanced artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning capabilities.

The Evolution of Snapdragon’s 5nm Processors
Snapdragon’s journey towards the development of 5nm processors is a story of constant innovation and technological breakthroughs. It began with larger scale processes and gradually evolved through the 10nm, 7nm, and finally, the 5nm process technology.
Each step of this evolution brought significant improvements. The transition from 10nm to 7nm, for example, increased transistor density by about 70%, leading to a substantial boost in processing power and energy efficiency. The subsequent transition to the 5nm process represented an even more dramatic improvement, allowing for around 80% more logic density compared to 7nm technology.
Comparing with previous generations, 5nm processors perform tasks more quickly and efficiently. For instance, when compared to a 7nm processor, a 5nm chip can deliver 15% faster speed while consuming 30% less power. These advancements have greatly improved the user experience by enabling faster, smoother operation of devices, longer battery life, and superior multitasking capabilities.
Snapdragon’s 5nm Processor Line-Up
Snapdragon’s 5nm processor portfolio currently consists of several high-performance models, including:
- Snapdragon 888: This flagship processor, released in 2020, is used in high-end smartphones like the Samsung Galaxy S21 and the Xiaomi Mi 11. The Snapdragon 888 offers an integrated 5G modem, an AI Engine capable of performing 26 trillion operations per second (TOPS), and superior graphics rendering with the Adreno 660 GPU.
- Snapdragon 888 Plus: Launched in mid-2021, this processor offers improved performance over its predecessor, the Snapdragon 888, boasting a 3GHz clock speed and AI performance of up to 32 TOPS.
- Snapdragon 870: This chip, announced in early 2021, is an enhanced version of the Snapdragon 865 Plus, offering a higher clock speed for even more impressive performance.
Each of these processors carries its unique specifications and is designed for different types of devices, delivering varying levels of performance to cater to the needs of different user segments.
In-Depth Look at Key Snapdragon 5nm Processors
Snapdragon 888: The Snapdragon 888 is built on the 5nm process technology, offering substantial improvements over its predecessors. It comprises an 8-core CPU, with one Cortex-X1 core running at 2.84GHz, three Cortex-A78 cores at 2.42GHz, and four power-efficient Cortex-A55 cores at 1.8GHz. The integrated X60 5G modem-RF system allows for global compatibility and 5G speeds, enabling faster download and upload speeds for mobile devices.
Furthermore, the Snapdragon 888 includes advanced AI capabilities with its 6th generation Qualcomm AI Engine. It’s capable of performing 26 TOPS, a remarkable leap forward in mobile AI performance that empowers users with enhanced photography, gaming, and voice assistant capabilities.
Snapdragon 888 Plus: The Snapdragon 888 Plus pushes the performance envelope even further. It retains most of the core specifications of the Snapdragon 888 but enhances the maximum clock speed to 3.0GHz. The AI performance is also boosted, with the ability to perform up to 32 TOPS, enhancing the user experience in gaming, photography, and voice assistant applications.
Snapdragon 870: Positioned as a high-performance processor that delivers great value, the Snapdragon 870 offers a 3.2GHz CPU clock speed. It retains many of the features of the Snapdragon 865 Plus, such as the Snapdragon Elite Gaming features and the 5th generation AI Engine but provides a performance boost thanks to the 5nm process technology.
The Future of 5nm Technology in Snapdragon Processors
The future of 5nm technology in Snapdragon processors looks promising. As the tech world demands ever more powerful and efficient devices, Snapdragon is expected to continue pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with 5nm technology.
Future processors might see increased performance and energy efficiency, as well as further miniaturization. This will enable more complex AI and machine learning capabilities, improved graphics and gaming performance, and better battery life.
Moreover, the development of 5nm technology also paves the way for advancements in areas such as the Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous vehicles, and 5G technology, where high-performance, energy-efficient processing is critical.
Conclusion
The landscape of processor technology is continuously evolving, with Snapdragon’s 5nm processors offering a glimpse into the future. They deliver superior performance and energy efficiency, shaping the user experience in mobile and connected devices. As we’ve explored the various 5nm processors in Snapdragon’s lineup, the impact of this technology becomes clear. It’s not just about power; it’s about enabling new possibilities in mobile technology, from advanced AI to immersive gaming experiences. As we look forward, the potential of 5nm technology and its implications for Snapdragon processors is boundless, promising exciting advancements in the realm of digital innovation.
-

 Phones6 months ago
Phones6 months agoHow Do I Know if My Phone Supports AR?
-

 Tech6 months ago
Tech6 months agoDoes Astigmatism Affect Your VR Experience?
-

 Business5 months ago
Business5 months agoHow Do You Make an AR Without Coding?
-
 Phones5 months ago
Phones5 months agoWhat To Do About That Weird Notification Sound on Android?
-
 Tech5 months ago
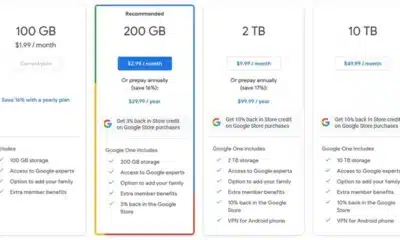
Tech5 months agoHow Can I Get Google Drive 1TB for Free?
-

 Phones5 months ago
Phones5 months agoHow Does SnapDrop Work? – Instant File Sharing Made Easy
-

 Tips and Tricks5 months ago
Tips and Tricks5 months agoCan You Use Windows VR for Sculpting?
-
 Tech4 months ago
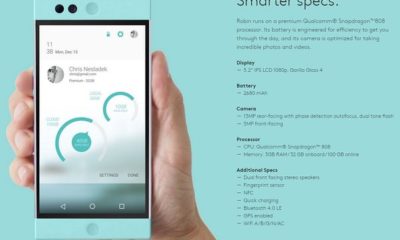
Tech4 months ago5 things you’ll miss after switching to iPhone from Android





















